Frequently Asked Questions
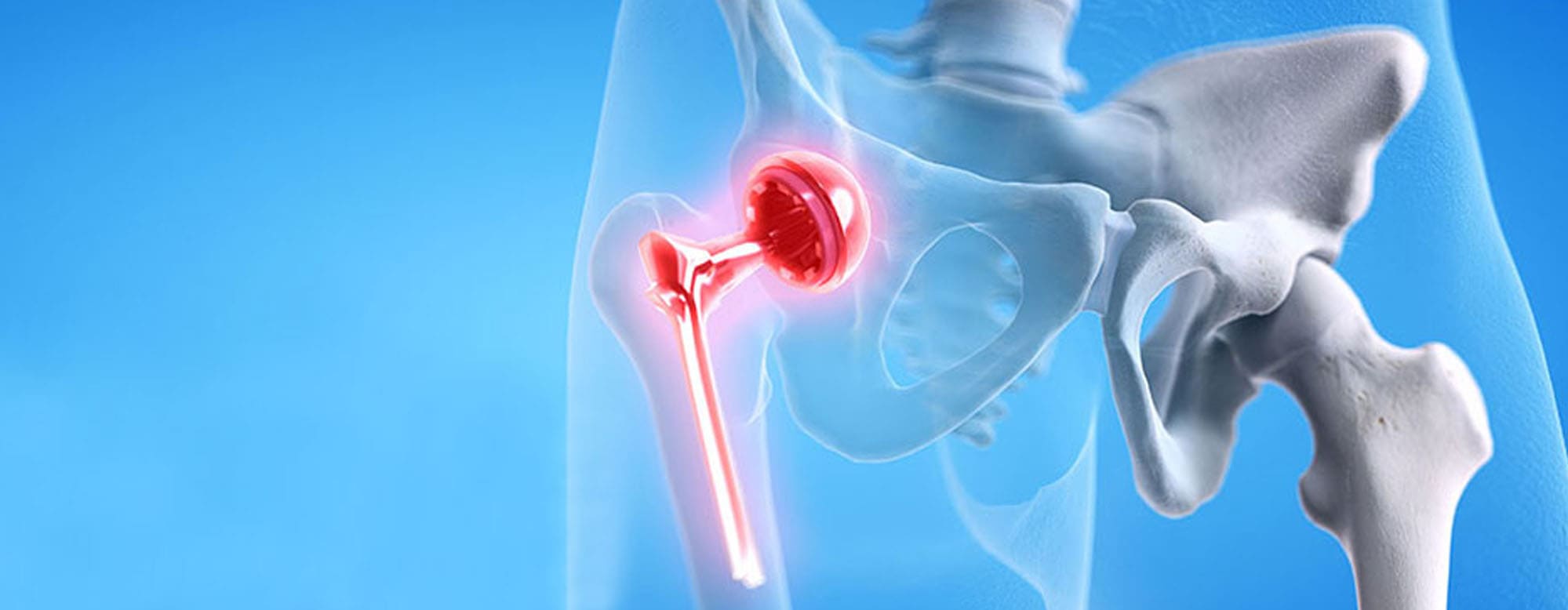
Primary Hip Replacement
Primary hip replacement refers to a surgical procedure in which an artificial implant replaces the hip joint that may be either damaged or arthritic. It is relatively common to ease pain and increase movement in someone who has acute arthritis of the hip or other hip joint problems.
Candidates for hip replacement surgery usually have severe pain in the hip and stiffness that limit daily activities, including walking or climbing stairs, and for which other treatments such as medication or physical therapy have provided little to no relief. We will evaluate your overall health, age, and activity level to determine whether hip replacement is suitable for you.
Although hip replacement is generally safe, the possible risks from the surgery include infection, blood clots, hip dislocation, differences in leg length, and less commonly, loosening or failure of the implant. It is an effort for surgeons to reduce the possibility of some of these risks occurring. Technology and techniques have advanced, therefore making the operation much safer on the whole.
Recovery generally includes time in the hospital followed by physical therapy to recover strength and mobility. Most patients are able to walk with support within a few days of the surgery and continue to progress during the weeks thereafter. Complete recovery may take several months, during which the patient is advised to avoid high-impact activities and sharp movements to prevent injury to the new hip.
Hip replacements are now made to last 15 to 20 years or more, depending on activity level, age, and implant type. Some patients will not require any re-operations in their lifetime; however, some younger or highly active patients may need a revision hip replacement if the bearing surface wears out over time.
Revision Hip Replacement
Revision hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which an older implant of hip replacement is removed and replaced with a new one. This operation is generally necessary when a previous hip replacement has failed due to a number of reasons, such as wear and tear, loosening, infection, or dislocation.
Revision hip replacement may be needed because of pain, infection, loosening of the implant, fractures involving the implant, or mechanical failure of the original hip replacement. We will examine your implant and the surrounding bone and tissue to determine if a revision is appropriate.
As with any surgery, there are risks with revision hip replacement: possible infection, blood clots, fracture of surrounding bone, injury to nerves or blood vessels and loosening of the implant however Improvements in surgical techniques and post-operative care have minimized these risks.
Recovery from revision surgery may be more complicated and, in some instances, take a little longer than your first hip replacement surgery. Since many revision surgeries involve tissues that may have some scarring, bone loss has occurred, or good tissue has been compromised, patients may require additional rehabilitation with an extended recovery period.
Most patients after recovery experience increased mobility and a decrease in pain, though results will vary based upon such mitigating factors as age, general health of the patient, and the reason for revision. Physical therapy is often prescribed to help the patient regain muscle strength, mobility, and function of the hip.
Pelvic Acetabular Fracture
A pelvic acetabular fracture is a break in the acetabulum, the part of the pelvis that forms the socket of the hip joint where the femoral head sits (the top of the thigh bone). These fractures generally occur in high-impact trauma, as in car accidents or falls, and can be serious due to the proximity to major vessels and organs.
The common symptoms include severe pain in the hip, pelvis, or groin area, inability to move or bear weight on the affected leg, swelling, and bruising around the hip or pelvis. The patients might even feel some degree of numbness or weakness in the leg if nerves are involved.
The diagnosis generally consists of physical examination, X-rays, and very often a CT scan in order to achieve a detailed view of the fracture. This CT scan will help the surgeon understand the pattern of fracture, displacement, and the extent of damage-all critical knowledge for treatment planning.
Pelvic acetabular fracture treatment differs with respect to the type of fracture, age, and health of the individual. The conservative mode of treatment pertaining to small fractures involves rest and physical therapy. However, for major fractures, surgical intervention becomes necessary as bones may get displaced and need proper realignment. Surgical options to repair the fracture may use screws and plates or other hardware to allow the joint to heal properly.
The extent of recovery also varies depending on the extent of the fracture and which path the treatment will take. Surgical patients could require limited weight-bearing function in the affected limb for several weeks, while others have to consider additional physical therapy work for full recovery of strength and motion. The overall recovery may take several months, with varied residual stiffness or limitation of motion, depending on the complexity of the injury and response to treatment.
Hip Fracture In Old Age
The reason why elderly people are more prone to hip fractures includes the occurrence of contributing factors that include a decline in bone density, loss of muscle strength, and imbalance; this contributes to an increased tendency to fall. Other age-related factors include poor eyesight or medications leading to dizziness, which can make them more likely to fall and hence fracture some bones.
Symptoms often include severe pain in the hip or groin, inability to stand on the involved leg, and unable to stand or walk. Some individuals also show bruising, swelling, and outward turning of the affected leg. If the fracture is not that serious, the pain may not be that great, but hip pain after a fall should receive medical attention.
Treatment usually involves surgery to repair or replace the fractured hip. Options include internal fixation, where metal screws or plates are used; partial hip replacement; or total hip replacement, depending on the type of fracture and overall health of the patient. Often, surgery is followed by physical therapy and rehabilitation for assistance in recovery and mobility.
Recovery depends on the patient’s age, health condition, and type of fracture. Treatment is generally based on physical therapy to regain muscle strength, balance, and mobility. Some patients may require temporary or long-term aid in walking or daily activities. Recovery can take several months, and many people will experience lingering effects such as reduced mobility or increased risk of future fractures.
Prevention of hip fracture involves the reduction of risk factors for falls and the improvement of bone health through exercises to maintain strength and balance, a diet containing calcium and vitamin D, medication to enhance bone density where this may be necessary, and modifications around the home to make it safer. Regular checks on vision and reviews of medications can also minimize risks of falls.
Fracture around Total Hip Replacement
A Periprosthetic hip fracture is the condition in which there is a break in the bone surrounding the hip implant following a total hip replacement. These fractures may be due to trauma, such as a fall, or due to bone weakening over time, as with osteoporosis. They are relatively uncommon but often quite problematic to treat and recover from.
Symptoms may include sudden, severe pain around the hip or thigh region, inability to bear weight through the affected leg, or an obvious deformity resulting in either an apparent change in leg alignment or length. Other signs could be swelling, bruising, or limitation of movement of the hip. Any significant pain following trauma in a hip replacement patient should be checked as soon as possible.
Treatment will vary regarding the type of fracture, location, and severity, along with the implant status. It can sometimes be non displaced and treated with rest and limited mobility. However, surgical intervention is most often required. Surgical options include fixation with screws or plates, or in some cases, replacing part or all of the hip implant if that has become loose or damaged.
Recovery usually entails a combination of protected weight-bearing, physical therapy, and close follow-up with the treating team. Depending on the nature of the procedure, the overall health status, this rehabilitation can last several months. Some patients need to use walking aids like crutches and walkers, and physical therapy is also essential for regaining muscle and range of motion.
The principle of prevention is founded on the reduction of risks of falls, as well as on maintaining good bone health through regular exercise, proper intake of calcium and vitamin D, and medication to enhance bone density. The aggravation of symptoms can be effectively prevented by making a home safer, including the removal of tripping hazards, and using assistive devices when needed. Regular follow-ups with the orthopedic surgeon will help in keeping a track of the stability of the implant against early signs of weakening of bones around the replacement.